The peer-review process is a critical step in academic publishing that ensures research quality, credibility, and scholarly integrity. Researchers submitting their work to reputable journals must undergo a rigorous evaluation by experts in the field. This guide provides insights into what to expect during the peer-review process.
1. Overview of the Peer-Review Process
The peer-review process serves to:
- Ensure Research Quality: Experts evaluate the validity, originality, and impact of the study.
- Enhance Credibility: Peer-reviewed articles gain recognition and trust within the academic community.
- Provide Constructive Feedback: Reviewers offer suggestions for improving clarity, methodology, and argumentation.
- Filter Submissions: Journals maintain high publication standards by accepting only well-researched and impactful studies.
2. Types of Peer Review
Different journals use various peer-review models, including:
- Single-Blind Review: Reviewers know the author’s identity, but the author does not know the reviewers.
- Double-Blind Review: Both the author and reviewers remain anonymous, ensuring unbiased feedback.
- Open Peer Review: Both the author and reviewers know each other’s identities, promoting transparency.
- Post-Publication Peer Review: Research is published first, and peer review happens publicly afterward.
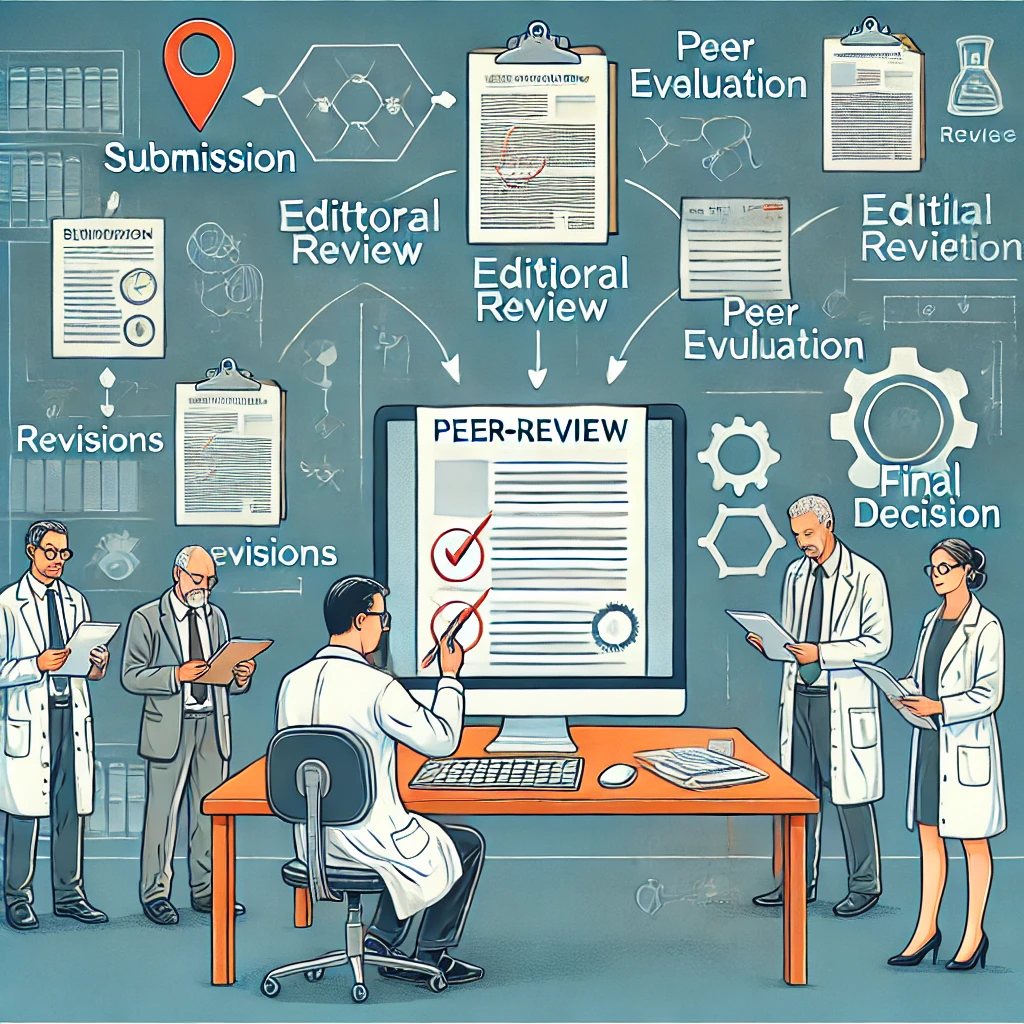
3. Steps in the Peer-Review Process
1. Submission of the Manuscript
- The author submits the manuscript according to the journal’s formatting and submission guidelines.
- An initial screening checks for compliance with journal scope and quality requirements.
2. Editorial Assessment
- The editor evaluates the manuscript’s originality, significance, and adherence to submission standards.
- If the manuscript meets the criteria, it is sent for peer review; otherwise, it may be rejected or returned for revisions.
3. Peer Review and Evaluation
- The manuscript is assigned to subject-matter experts who assess its quality, methodology, and contribution to the field.
- Reviewers provide feedback, which may include:
- Acceptance with Minor Revisions – Small corrections needed.
- Major Revisions Required – Significant improvements needed before reconsideration.
- Rejection – The manuscript does not meet the journal’s standards.
4. Author Revisions
- The author revises the manuscript based on reviewer feedback and submits a revised version with a detailed response.
- The revised manuscript may undergo further review before final acceptance.
5. Final Decision and Publication
- The editor makes a final decision based on the reviewers’ recommendations.
- Accepted papers go through copyediting and formatting before publication.
4. Best Practices for Navigating the Peer-Review Process
To increase your chances of successful publication:
- Follow Submission Guidelines: Ensure proper formatting, citations, and manuscript structure.
- Address Reviewer Feedback Thoroughly: Provide clear responses to all comments and make necessary improvements.
- Be Patient and Professional: The review process can take weeks to months; remain patient and open to feedback.
- Choose the Right Journal: Submit your work to journals that align with your research area and publication goals.
5. Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
- Delayed Review Process: Some journals take longer due to reviewer availability; choose journals with a reliable timeline.
- Harsh Criticism: Reviewers may provide critical feedback; treat it as an opportunity to refine your work.
- Rejection: If rejected, revise your manuscript based on feedback and submit to another suitable journal.
Final Thoughts
The peer-review process is an essential component of scholarly publishing, ensuring high-quality research reaches the academic community. By understanding the steps involved and preparing for constructive feedback, researchers can successfully navigate the process and improve the impact of their work.